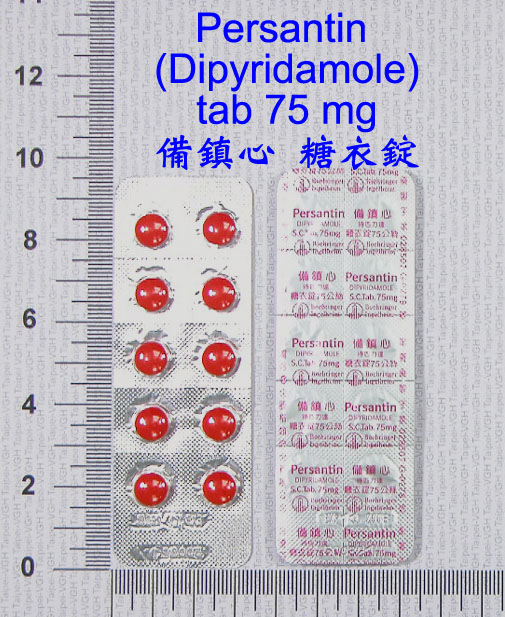
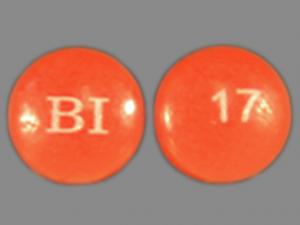
現在位置 : 藥物 > 雙嘧達莫 Dipyridamole - 潘生丁 (備鎮心) - Persantine
|
雙嘧達莫 (Dipyridamole)- 潘生丁 (Persantine)
雙嘧達莫(Dipyridamole,中華藥典名:二吡待摩,商品名 潘生丁 (備鎮心) Persantine),是一種擴張冠脈及抗血栓形成的藥物。主要用於缺血性心臟病及中風,也少量用於其他疾病的治療。 副作用可有頭痛、眩暈、噁心、嘔吐、腹瀉等不良反應; 與肝素合用可引起出血傾向; 偶發皮疹,冠狀動脈盜血現象。 適應症:對於慢性狹心症之治療可能有效 藥物作用: 本藥為一種「防止血液凝固」及「預防心絞痛發作」的藥物。有防止血液凝固的作用,因此可用來預防手術後凝固的小血塊經由血液循環到達心臟,造成心臟微血管阻塞,導致心臟缺氧而壞死。本藥亦為一種預防心絞痛的藥物。心絞痛的發生主要是由於心臟血管的收縮,使負責攜帶氧氣的血液不能順暢流入心臟,更由於氧氣的缺乏,造成心臟細胞的壞死及疼痛。本藥的作用,就是能使心臟的血管放鬆,讓更多的氧氣經由血液流入心臟,預防心絞痛的發作。 藥理作用: (1). 直接擴張冠狀動脈來增加心肌的血流量,還可促進生病之心臟的副血行路循環的發展。 (2). 高劑量可提高血小板Cyclic AMP的形成,故又可阻斷ADP誘發的凝集反應,而抑制血小板的粘著凝集,故能防止血栓的形成。 用法: 本藥最好在飯前一小時服用,同時並飲用一杯水,以幫助吞嚥及減少藥物可能對胃部的刺激。如有必要時,此藥的藥片可以壓碎服用。如果無法忍受此藥對胃部的刺激,亦可與食物或牛奶一起服用。 副作用/警語:頭痛、眩暈、噁心、體肢潮紅,胃腸稍不適 副作用可能有頭痛、眩暈、噁心、嘔吐、腹瀉等不良反應; 與肝素合用可引起出血傾向; 偶發皮疹,冠狀動脈盜血現象。 禁忌症:對Dipyridamole藥物或其賦形劑成分過敏者不該使用此藥。 |
|
注意事項
服用此藥後,可能會產生輕微頭暈目眩的副作用,尤其在剛開始服藥期間。因此在尚末完全適應此藥之前,當開車或操作危險機械時,必須小心謹慎。 如果懷孕,對藥物過敏,或者有心臟疾病﹑血液凝固方面的問題﹑低血壓﹑肝臟疾病等等,醫師需要針對這些情況謹慎用藥,因此在使用此藥之前,應該事先通知醫師。 此藥會抑制血液的凝固而使流血的時間增長,因此在拔牙或動手術之前,應該事先通知醫師,以免手術進行中造成過量的流血。 此藥的作用,主要是用於預防心絞痛的發生,並不是用來當作心絞痛急性發作時的藥物使用。如果感覺到心臟疼痛時,應該使用另外一種醫師的處方藥物,如硝基甘油(Nitroglycerin)等,來做急救。 為了更有效預防血液凝固,醫師也許會要求同時服用阿斯匹靈或其它抗凝血的藥物。由於兩種藥物一起使用,可能會使流血的機會相對地增高。為了降低此一危險性,應該完全遵照醫師的指示劑量服用。如果購買成藥時,應該詳細詢問藥師所購買的藥物是否含有阿斯匹靈或其它抗凝血的成分,以免造成藥物過量的危險。 經過一段時間藥物治療後,即使覺得心臟已經恢復正常,亦不可間斷或者突然停止服藥。突然停藥有可能使心臟的情況惡化。如有停藥的必要時,應該事先得到醫師的許可,並且在指示下漸漸降低服藥約次數或劑量,然後再停藥。 副作用 Dipyridamole最常見的副作用為:腹部不適(6.1%),噁心(4.6%)頭暈(12%),頭痛(2.3%)。其它可能副作用包括:胃部輕微的抽痛﹑腹瀉﹑面部潮紅﹑皮膚瘙癢﹑噁心嘔吐﹑虛弱等,這些副作用,通常在服用藥物一陣子後,應該會漸漸消失。不過,如果這些副作用達到困擾你的程度,或者經過一段時間後,還不能完全消除,就應該通知醫師。 此藥較嚴重的副作用為:皮膚起紅疹﹑胸口疼痛﹑暈倒。通常這些副作用發生的機率較低,但是如果發生時,此可能是藥物造成的不良反應,或者是劑量需要調整。應該盡快通知醫師。 |
|
Dipyridamole (Persantine)
Dipyridamole (trademarked as Persantine) is a medicine that inhibits thrombus formation when given chronically and causes vasodilation when given at high doses over a short time. Mechanism and effects Dipyridamole inhibits the phosphodiesterase enzymes that normally break down cAMP (increasing cellular cAMP levels and blocking the platelet response to ADP) and/or cGMP (resulting in added benefit when given together with nitric oxide [NO] or statins). It inhibits the cellular reuptake of adenosine into platelets, red blood cells and endothelial cells leading to increased extracellular concentrations of adenosine. Medical uses ● Dipyridamole has been shown to lower pulmonary hypertension without significant drop of systemic blood pressure. ● It inhibits formation of pro-inflammatory cytokines (MCP-1, MMP-9) in vitro and results in reduction of hsCRP in patients. ● It inhibits proliferation of smooth muscle cells in vivo and modestly increases unassisted patency of synthetic arteriovenous hemodialysis grafts. ● It increases the release of t-PA from brain microvascular endothelial cells. ● It results in an increase of 13 - HODE and decrease of 12-HETE in the subendothelial matrix (SEM) and reduced thrombogenicity of the SEM. ● Pretreatment it reduced reperfusion injury in volunteers. ● It has been shown to increase myocardial perfusion and left ventricular function in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. ● It results in a reduction of the number of thrombin and PECAM-1 receptors on platelets in stroke patients. ● cAMP impairs platelet aggregation and also causes arteriolar smooth muscle relaxation. Chronic therapy did not show significant drop of systemic blood pressure. ● It inhibits the replication of mengovirus RNA. ● It can be used for myocardial stress testing as an alternative to exercise-induced stress methods such as treadmills. Use in individuals with a history of stroke Modified release dipyridamole is used in conjunction with aspirin (under the trade names Aggrenox in the USA or Asasantin Retard in the UK) in the secondary prevention of stroke and transient ischaemic attack. This practice has been confirmed by the ESPRIT trial. Dipyridamole absorption is pH-dependent and concomitant treatment with gastric acid suppressors (such as a proton pump inhibitor) will inhibit the absorption of liquid & plain tablets. Modified release preparations are buffered and absorption is not affected. It is not, however, licensed as monotherapy for stroke prophylaxis, although a Cochrane Review has suggested that dipyridamole may reduce the risk of further vascular events in patients presenting after cerebral ischaemia. A triple therapy of aspirin, clopidogrel, and dipyridamole has been investigated, but this combination led to an increase in adverse bleeding events. ● Via the mechanisms mentioned above, when given as 3 to 5 min infusion it rapidly increases the local concentration of adenosine in the coronary circulation which causes vasodilation. ● Vasodilation occurs in healthy arteries, whereas stenosed arteries remain narrowed. This creates a "steal" phenomenon where the coronary blood supply will increase to the dilated healthy vessels compared to the stenosed arteries which can then be detected by clinical symptoms of chest pain, electrocardiogram and echocardiography when it causes ischemia. ● Flow heterogeneity (a necessary precursor to ischemia) can be detected with gamma cameras and SPECT using nuclear imaging agents such as Thallium-201, Tc99m-Tetrofosmin and Tc99m-Sestamibi. However relative differences in perfusion do not necessarily imply any absolute decrease in blood supply in the tissue supplied by a stenosed artery. Other uses Dipyridamole also has non-medicinal uses in a laboratory context, such as the inhibition of cardiovirus growth in cell culture. Dipyridamole overdose Dipyridamole overdose can be treated with aminophylline which reverses its hemodynamic effects (vasodilation). Symptomatic treatment is recommended, possibly including a vasopressor drug. Gastric lavage should be considered. Administration of xanthine derivatives (e.g., aminophylline) may reverse the hemodynamic effects of dipyridamole overdose. Since dipyridamole is highly protein bound, dialysis is not likely to be of benefit. |
|
Persantine is used for:
Preventing blood clots after heart valve surgery. It is used in combination with anticoagulants (eg, warfarin). It also may be used for other conditions as determined by your doctor. Persantine is a platelet inhibitor. How it works is not fully understood. It is thought to work by increasing the levels of a body chemical (adenosine), which widens blood vessels and decreases platelet activity. Do NOT use Persantine if: •you are allergic to any ingredient in Persantine Contact your doctor or health care provider right away if any of these apply to you. Before using Persantine: Some medical conditions may interact with Persantine. Tell your doctor or pharmacist if you have any medical conditions, especially if any of the following apply to you: • if you are pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or are breast-feeding • if you are taking any prescription or nonprescription medicine, herbal preparation, or dietary supplement • if you have allergies to medicines, foods, or other substances • if you have severe heart disease, chest pain, low blood pressure, or liver problems, or you have recently had a heart attack Some MEDICINES MAY INTERACT with Persantine. Tell your health care provider if you are taking any other medicines, especially any of the following: • Adenosine because the risk of its side effects, including low blood pressure and irregular heartbeat, may be increased by Persantine • Anticholinesterases (eg, neostigmine) because their effectiveness may be decreased by Persantine This may not be a complete list of all interactions that may occur. Ask your health care provider if Persantine may interact with other medicines that you take. Check with your health care provider before you start, stop, or change the dose of any medicine. How to use Persantine: Use Persantine as directed by your doctor. Check the label on the medicine for exact dosing instructions. • Take Persantine by mouth on an empty stomach at least 1 hour before or 2 hours after eating. It may be taken with food if it upsets your stomach. • If you miss a dose of Persantine, take it as soon as possible. If it is almost time for your next dose, skip the missed dose and go back to your regular dosing schedule. Do not take 2 doses at once. Ask your health care provider any questions you may have about how to use Persantine. Important safety information: • Persantine may cause dizziness. These effects may be worse if you take it with alcohol or certain medicines. Use Persantine with caution. Do not drive or perform other possibly unsafe tasks until you know how you react to it. •Persantine may cause dizziness, lightheadedness, or fainting; alcohol, hot weather, exercise, or fever may increase these effects. To prevent them, sit up or stand slowly, especially in the morning. Sit or lie down at the first sign of any of these effects. •Tell your doctor or dentist that you take Persantine before you receive any medical or dental care, emergency care, or surgery. •Use Persantine with caution in the ELDERLY; they may be more sensitive to its effects. •Persantine should not be used in CHILDREN younger than 12 years old; safety and effectiveness in these children have not been confirmed. •PREGNANCY and BREAST-FEEDING: If you become pregnant, contact your doctor. You will need to discuss the benefits and risks of using Persantine while you are pregnant. Persantine is found in breast milk. If you are or will be breast-feeding while you use Persantine, check with your doctor. Discuss any possible risks to your baby. Possible side effects of Persantine: All medicines may cause side effects, but many people have no, or minor, side effects. Check with your doctor if any of these most COMMON side effects persist or become bothersome: Diarrhea; dizziness; flushing; headache; itching; stomach pain; vomiting. Seek medical attention right away if any of these SEVERE side effects occur: Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue); chest pain; fast heartbeat; hepatitis; pounding in the chest; swelling of throat. This is not a complete list of all side effects that may occur. If you have questions about side effects, contact your health care provider. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. To report side effects to the appropriate agency, please read the Guide to Reporting Problems to FDA. |